Passive and Active Information Gathering
Passive Information Gathering
Footprinting
Target: Hackersploit.org
What we are looking for IP Addresses: IPv4: 172.67.202.99 and 104.21.44.180 IPv6: 2606:4700:3036::ac43:ca63 and 2606:4700:3031::6815:2cb4 Directories hidden from search engines: /wp-admin/, /wp-content/uploads/wpo-plugins-tables-list.json Names Email Addresses Phone Number Physical Addresses Web technologies being used: Use add-on "BuiltWith" to detect what technologies are being used.
Obtain IP Address by: use host command, use whatis host to learn more about this command
host hackersploit.org┌──(kali㉿kali)-[~]
└─$ host hackersploit.org
hackersploit.org has address 104.21.44.180
hackersploit.org has address 172.67.202.99
hackersploit.org has IPv6 address 2606:4700:3031::6815:2cb4
hackersploit.org has IPv6 address 2606:4700:3036::ac43:ca63
hackersploit.org mail is handled by 0 _dc-mx.2c2a3526b376.hackersploit.org.Why does this website have two IPv4 Addresses?
The website is behind CloudFlare, which is a Firewall/Proxy
If you ever come across a website using two IPv4 addresses
You're dealing with some sort of proxy
Robots.txt It essentially allows you to specify what folders or what files you don't want search engines to index
sitemap.xml A file that provides search engines an organized way of indexing a website.
Helpful Addons
Builtwith - Web technology profiler tool that allows users to identify what technologies a website is using
Wappalyzer - A web browser extension and open-source software that uncovers the technologies used on websites. It can detect content management systems, web frameworks, e-commerce platforms, JavaScript libraries, analytics tools, and many other technologies.
Whatweb - A command-line tool used for website reconnaissance and information gathering. It can be used to detect what technologies a website is using, such as web servers, programming languages, and content management systems.
HTTRack- This can be used to download a mirror of a website so you can analyze the source code to learn more about the site, ex: find vulnerabilities, get an understanding of the website structure etc
Whois Enumeration
whois A query and response protocol that is widely used for querying databases that store the registered users or assignees of an internet resource, such as:
Domain Name
IP Address Block
Autonomous System
Website Footprinting With Netcraft
Netcraft can be used to enumerate information passively from a website. Netcraft correlates information such as:
WHOIS
SSL or TLS certs
Web Technologies being used
Name servers
This saves you time from doing manual work, as Netcraft provides a lot of information that would otherwise take more time to gather if done manually.
Using results from our internet data mining, find out the technologies and infrastructure of any site. Explore hostnames visited by users of the Netcraft extensions. Search by domain or keyword.
Important results given by Netcraft
Validity Period (Certificate)
Certificate Issuer/Country
Certificate Transparency
Country: US
Organizational unit: Not Present
Subject Alternative Name: sni.cloudflaressl.com, hackersploit.org, *.hackersploit.org
Validity period: From May 11 2022 to May 10 2023 (11 months, 4 weeks, 2 days)
SSLv3/POODLE or Heartbleed Vulnerable? No, not according to Netcraft
Web trackers
This tells you what web analytics/trackers are enabled on the site
Site technologies Profiler
Issuing organisation Cloudflare, Inc.
Issuer common name Cloudflare Inc ECC CA-3
Certificate Transparency

Sender Policy Framework A host's Sender Policy Framework (SPF) describes who can send mail on its behalf. This is done by publishing an SPF record containing a series of rules. Each rule consists of a qualifier followed by a specification of which domains to apply this qualifier to.
DNSSEC: This ensures personal data such as the owners name, address etc, is all redacted from the WHOIS query. Domain registered through namecheap Confirmed with registrar URL Creation date: 2018-04-05T11:27:07Z Renewed: 2022-12-22 Domain Expiration: 2024-04-05T11:27:07Z
As you can see in this WHOIS query, since DNSSEC is not being used in this webserver, information such as the Registration Organization, State/Province, Country, is not redacted.
DNS Recon
DNS Recon falls under passive information gathering, this is because we are not actively engaging any targets (DNS Servers), we are just gathering information from public sources.
We will be looking for information that will provide us with a better understanding as to how the target website or system is configured to run
DNSRecon DNSRecon is a Python script that provides the ability to perform: Check all NS Records for Zone Transfers. Enumerate General DNS Records for a given Domain (MX, SOA, NS, A, AAAA, SPF and TXT). Perform common SRV Record Enumeration. Top Level Domain (TLD) Expansion.
MX: Mail server address NS: Nameserver A: IPv4 Addresses AAAA: IPv6 Addresses TXT: A DNS Record in text format which contains information about a given domain
TXT Records also have information that helps external network servers and services handle outgoing email from your domain. SPF (Server Policy Framework): A type of DNS TXT record commonly used for email authentication. This lists all the servers authorized to send emails from a particular domain
Without SPF records, or other authentication records, an attacker can easily impersonate a sender and trick the recipient into taking action or sharing information they otherwise would not.
SPF records were created because the standard protocol for email (SMTP) does not inherently authenticate the "from" address in an email
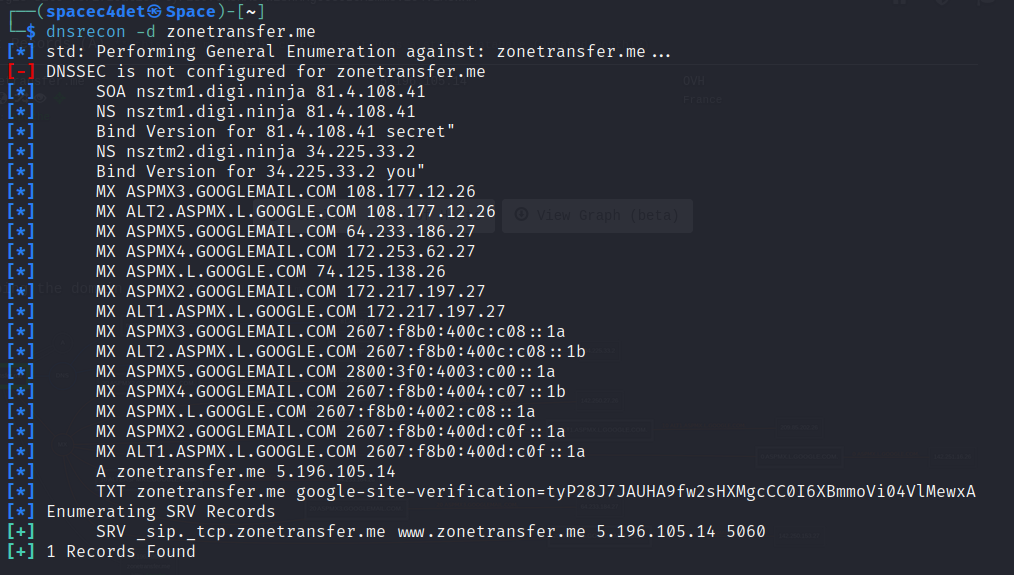
DNSRECON command
-d indicates we're providing a domain, in this case "hackersploit.org"

In the screenshot above we can see that the Mail server is displayed, this indicates CloudFlare doesn't hide proxy mail server addresses very well. MX: MX _dc-mx.2c2a3526b376.hackersploit.org 198.54.120.212
DNSDumpster A FREE domain research tool that can discover hosts related to a domain. Finding visible hosts from the attackers perspective is an important part of the security assessment process. Very similar to DNSRecon, but it has the advantage that the information displayed is organized fantasticly.
What is DNSDumpster A web-based tool used for gathering information about a target domain, including
Its subdomains
IP Addresses
Mail Servers
DNS Records
What is DNS Dumpster Commonly used for?
Reconnaissance
Security Auditing
Troubleshooting DNS Configurations
In addition, DNSDumpster provides a graphical user interface, and allows users to export data in various formats
It is important to use DNSDumpster ethically and responsibly
WAF with wafw00f
WAF stands for Web Application Firewall
wafw00f WafW00f is an open source tool used for detecting and fingerprinting web application firewalls (WAFs).
How does WafW00f work? It works by analyzing HTTP responses from a web application and searching for patterns and anomalies that are indicative of the presence of a WAF.
WafW00f is often used to test the effectiveness of WAFs and identify potential vulnerabilities in web applications.

Subdomain Enumeration With Sublist3r
What is Sublist3r? Sublist3r is a python-based open source tool used for subdomain enumeration. It works by querying multiple search engines, including Google, Yahoo, and Bing, as well as other sources such as certificate transparency logs, to generate a list of subdomains associated with a target domain
Sublist3r is commonly used to identify potential attack vectors, such as unsecured subdomains, misconfigured DNS records, and other security vulnerabilities. This tool should be used ethically and responsibly, as subdomain enumeration can be used for malicious purposes.

Google Dorking
Google Dorking, also known as Google hacking or Google-fu, is the practice of using advanced Google search techniques to locate sensitive or confidential information that is not easily accessible through simple searches.
Examples Limit search results to a domain,
site:ine.com
Limit results to URL: inurl:[word]
inurl:admin (ine.com/admin.php)
Limit results to subdomains: site:*.[domain]
site:*.ine.com
Limit results to site title: intitle:[word]
intitle:admin
Limit results to file type: filetype:[file type]
filetype:pdf
Limit results to indexes: intitle: index of
This results with indexes of a website
Find older cached versions of a website: cache:[domain]
cache:ine
Waybackmachine or Archive.org, has snapshots of older versions of websites
ExploitDB Google Hacking Database
A database of google dorks that have found useful info such as users, passwords, etc.
Email Harvesting with theHarvester
TheHarvester, a tool similar to Sublist3r, uses OSINT tools to find emails that belong to a domain that may be publicly available or found by crawling a leaked database.
Leaked Password Databases
Active Information Gathering
DNS Zone Transfers
DNS or Domain Name System, is used to translate human-readable domain names into IP Addresses that are used by computers to identify and communicate with each other over the internet.
How does DNS work? DNS works by maintaing a distributed database of domai names and their corresponding IP Addresses. When a user types in a domain name in their web browser, the browser sends a DNS query to a DNS server, which then looks up the corresponding IP Address and returns it to the browser.
How do DNS Zone Transfers work? DNS Zone Transfers are a mechanism used to replicate DNS databases between primary and secondary DNS servers. When a primary DNS server is updated with new DNS resource records, it notifies secondary DNS servers that are configured to replicate the zone. The secondary DNS servers then request a copy of the updated DNS database from the primary DNS server using a zone transfer.
DNS Records
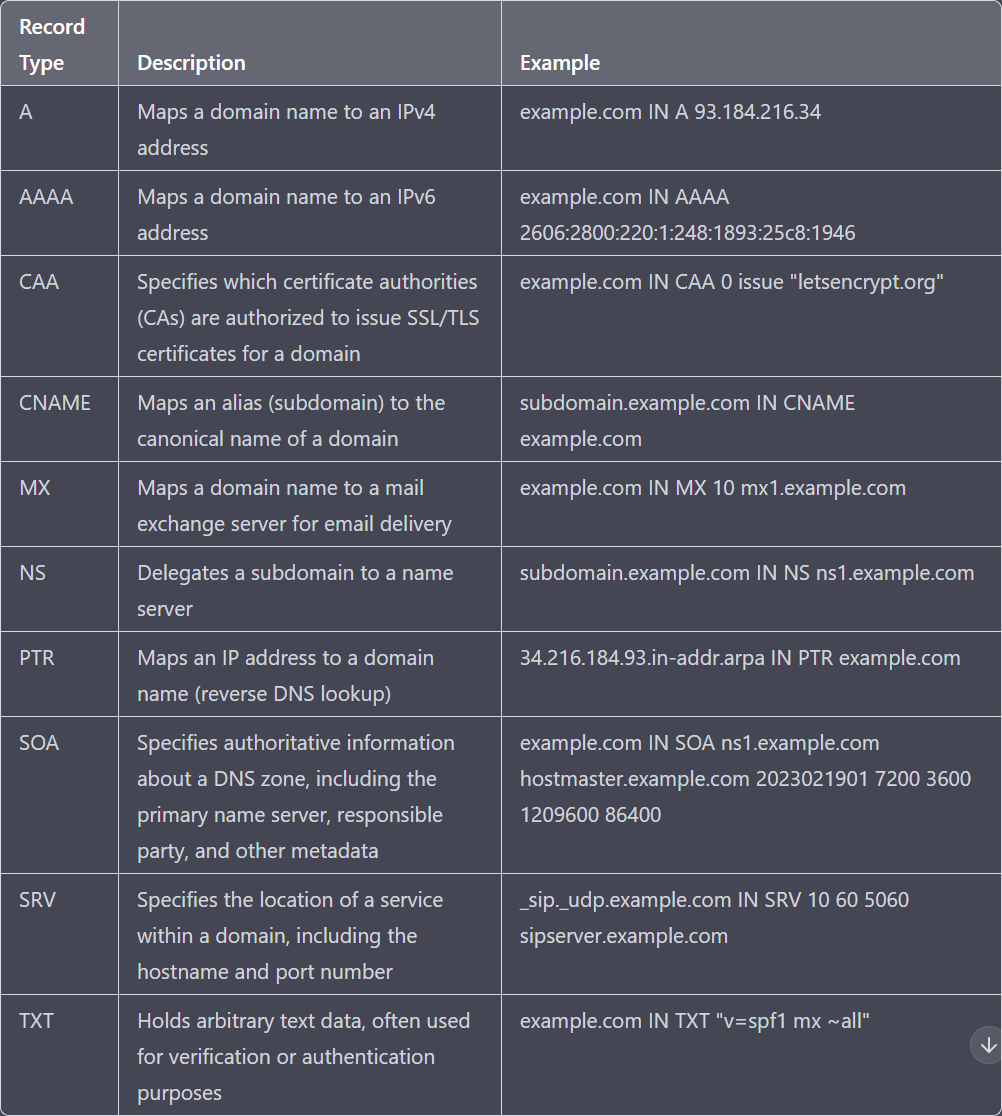
DNS Interrogation
DNS Interrogation is the process of enumerating DNS Records for a specific domain. It can be used to diagnose and troubleshoot DNS-related issues, such as identifying the cause of DNS resolution failures or misconfigured DNS records.
It can also be used to perform reconnaissance and obtain information about a target network or domain. Therefore, it is important to ensure that proper security measures are in place to protect against unauthorized DNS interrogation or exploitation.
DNSDumpster Result: zonetransfer.me
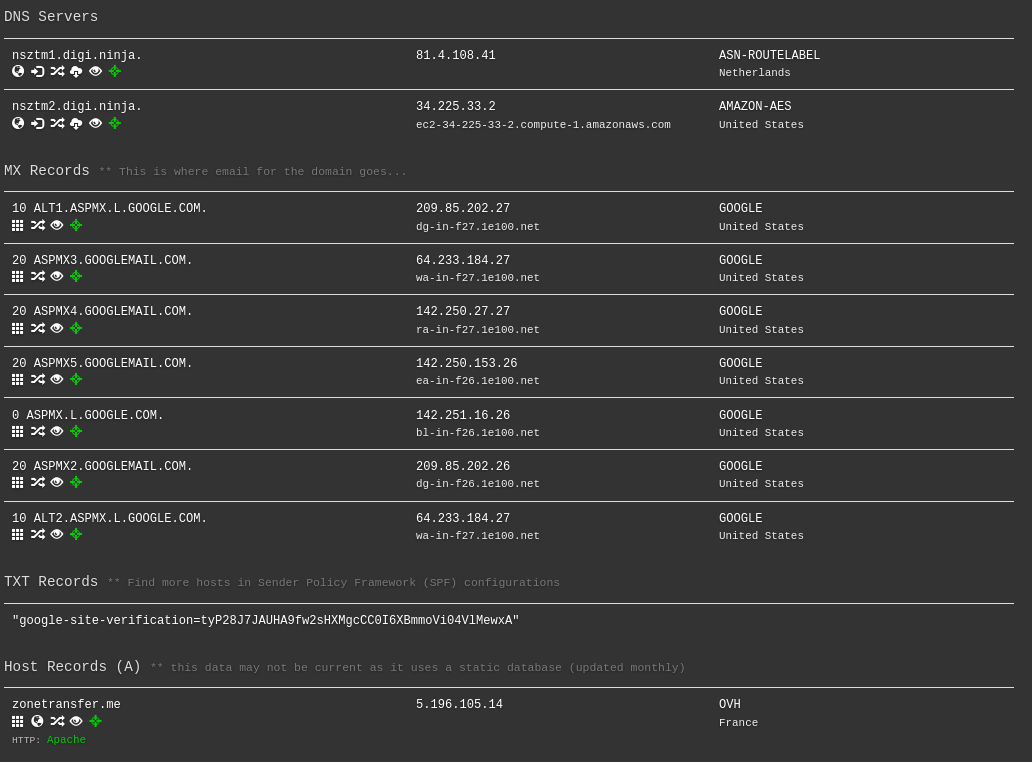
DNSDumpster Result: zonetransfer.me
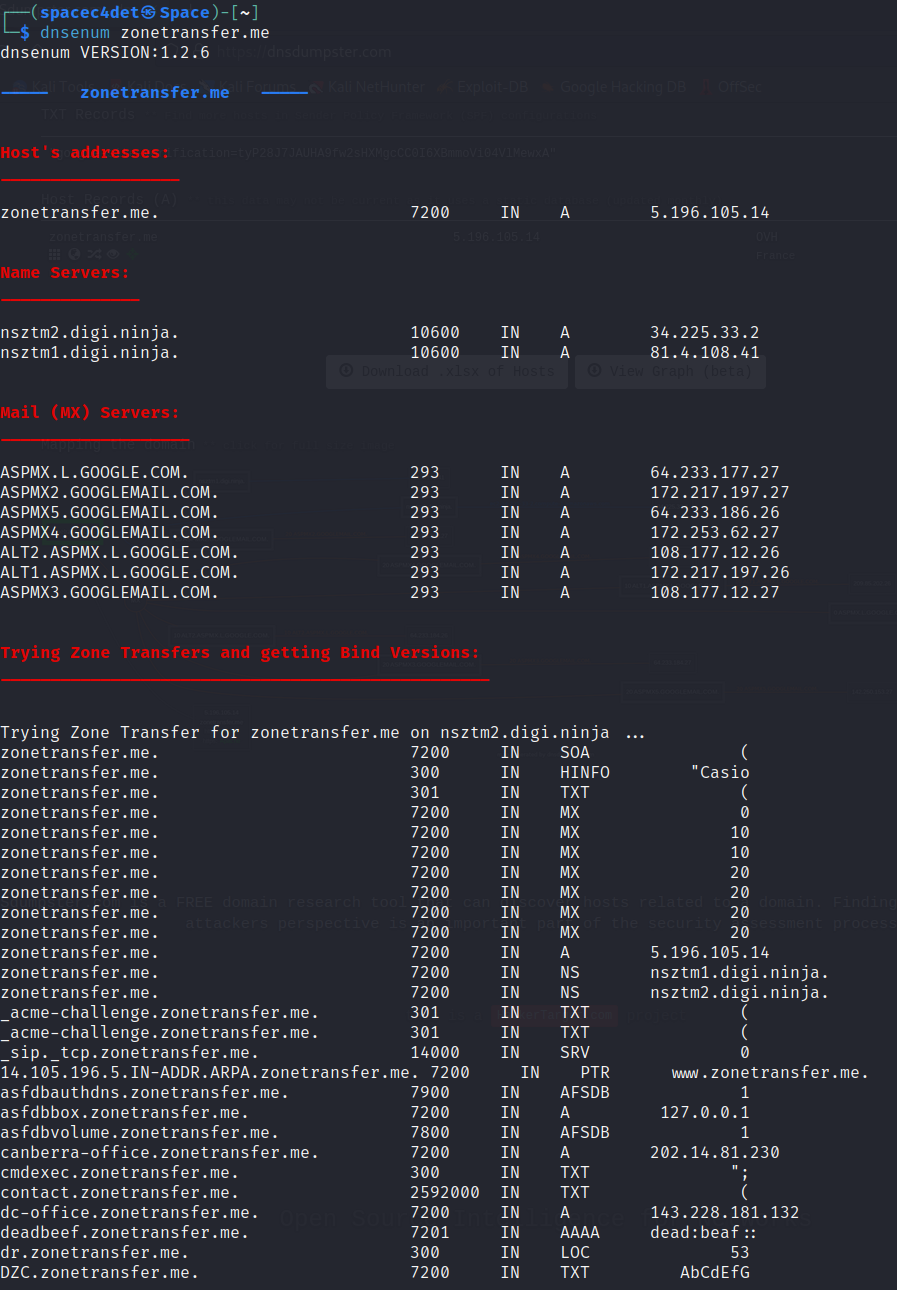
DNSEnum
Nmap Demo
Host Discovery with NMap
Finding your Home network IP and subnet.
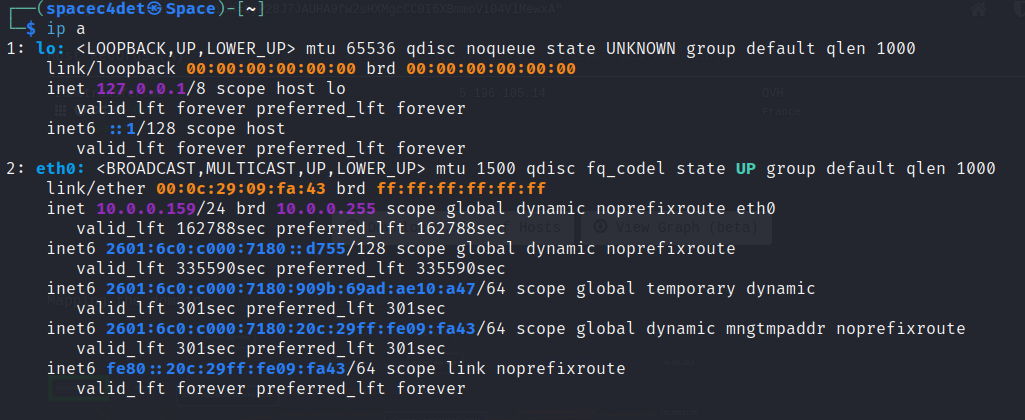
Using the -sn argument,
nmap -sn 10.0.0.0/24
Using nmap with the -sn switch tells Nmap to perform a "ping scan" of the IP addresses in the range 10.0.0.0 to 10.0.0.255 and report which hosts are up and running, without performing a port scan.
Nmap Results
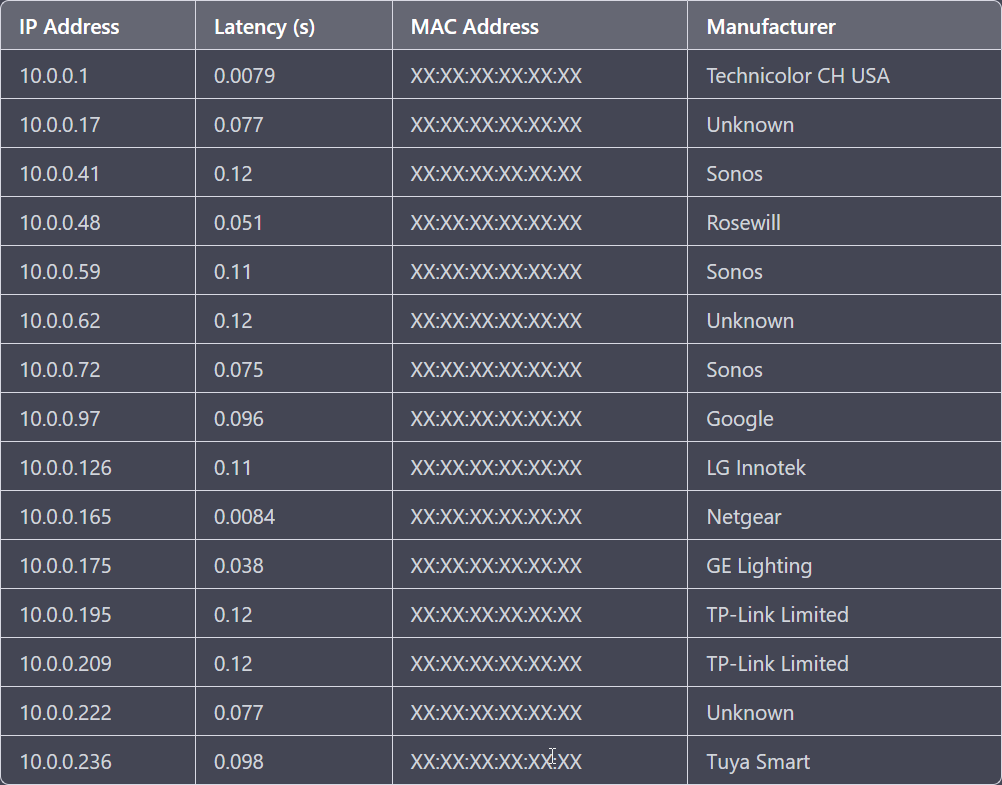
Netdiscover An open-source network address discovery tool that is used to discover hosts and devices on a local area network (LAN). It actively sends ARP requests and listens to ARP replies to identify devices and their associated MAC addresses, IP addresses, and vendor information
Netdiscover can be useful for network administrators who want to identify all the devices on a network or identify unauthorized devices. It can also be used to scan for vulnerable devices on a network.
How do Netdiscover and Nmap differ?
Nmap:
A network exploration tool that scans a network for hosts, services, and vulnerabilities.
Conducts a comprehensive port scan and identifies the services running on those ports.
Can perform a variety of advanced techniques such as OS detection, version detection, and service enumeration.
Netdiscover:
A network exploration tool that scans a network for live hosts and provides basic information such as MAC address and manufacturer.
Uses ARP (Address Resolution Protocol) to discover live hosts on a network.
Does not provide detailed information about the services running on hosts.
Nmap Lab
Here we ran ip a to find the IP Address of the Kali Machine we are using to perform Nmap scans.
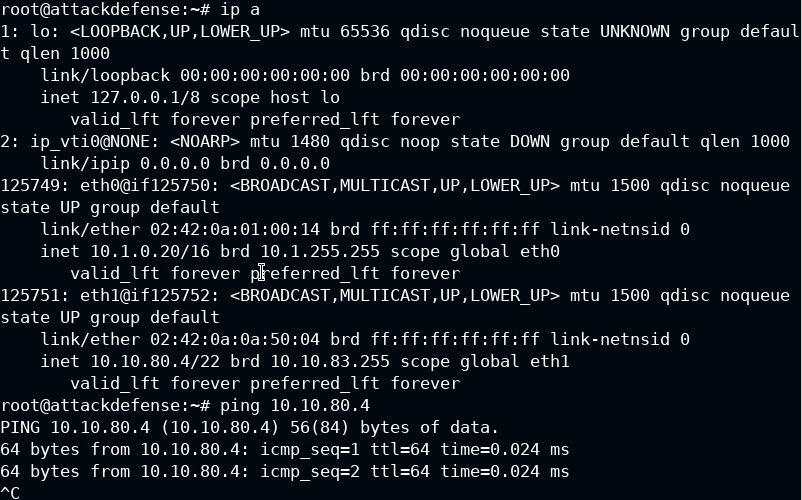
We then used the ping command to determine if our target host is up or not.
Nmap Port Scan
We then ran our first nmap scan against our target 10.4.16.154 which determined that the target was blocking ping probes, which indicated we needed to use -Pn , this switch tells Nmap to do no ping, which skips the host discovery stage altogether.
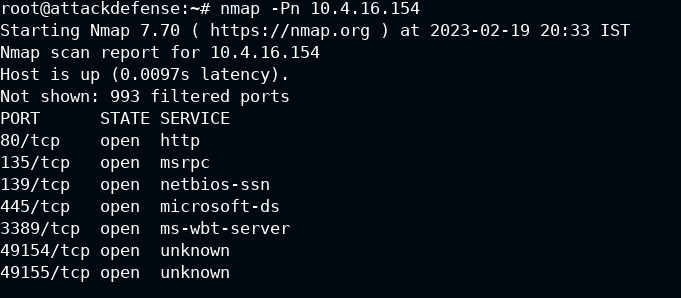
In the screenshot above, we can see that now nmap was able to discover the target host's open ports to identify the running services and applications.
Then we performed the same scan but added the -sV switch (Version detection), which tells Nmap to send a series of probes to determine the versions of the services and applications running.
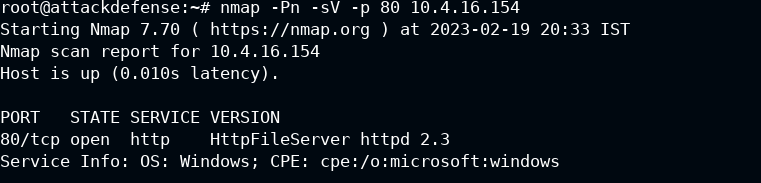
Last updated